共计 3039 个字符,预计需要花费 8 分钟才能阅读完成。
实验内容:对一副图像加噪,进行几何均值,算术均值,谐波,逆谐波处理,显示图像的结果
导入图像
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = cv.imread("1.png", 1)
img = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# cv.imshow("img.png", img)
plt.imshow(img)
添加随机盐噪声
# 加噪声
(rows, cols, chn) = img.shape
salt_img = np.copy(img)
for i in range(100):
x = np.random.randint(0, rows)
y = np.random.randint(0, cols)
salt_img[x, y, :] = 255
# cv.imshow("noise", img)
plt.imshow(salt_img)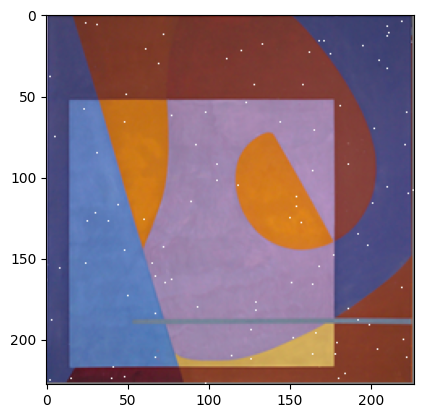
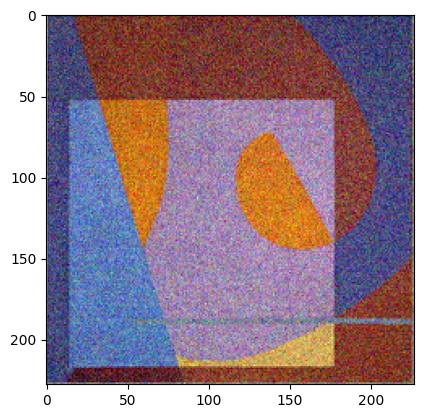
添加高斯噪声
from skimage import util
gauss_img = util.random_noise(img, mode='gaussian', mean=0, var=0.01)
plt.imshow(gauss_img)
几何均值滤波器
def geometric_mean_operator(roi):
roi = roi.astype(np.float64)
p = np.prod(roi)
return p ** (1 / (roi.shape[0] * roi.shape[1]))
def geometric_mean(image):
new_image = np.zeros(image.shape)
image = cv.copyMakeBorder(image, 1, 1, 1, 1, cv.BORDER_DEFAULT)
for i in range(1, image.shape[0] - 1):
for j in range(1, image.shape[1] - 1):
new_image[i - 1, j - 1] = geometric_mean_operator(image[i - 1: i + 2, j - 1: j + 2])
new_image = (new_image - np.min(image)) * (255 / np.max(image))
return new_image.astype(np.uint8)
def rgb_geometric_mean(image):
r,g,b = cv.split(image)
r = geometric_mean(r)
g = geometric_mean(g)
b = geometric_mean(b)
return cv.merge([r, g, b])geometric_mean_img = rgb_geometric_mean(gauss_img)
plt.imshow(geometric_mean_img)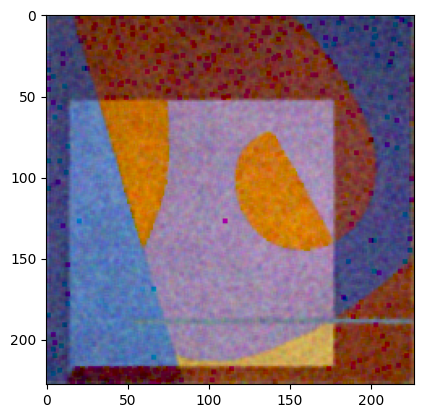
算数均值滤波
def arithmetic_mean(image):
new_image = np.zeros(image.shape)
image = cv.copyMakeBorder(image, 1, 1, 1, 1, cv.BORDER_DEFAULT)
for i in range(1, image.shape[0] - 1):
for j in range(1, image.shape[1] - 1):
new_image[i - 1, j - 1] = np.mean(image[i - 1: i + 2, j - 1: j + 2])
new_image = (new_image - np.min(image)) * (255 / np.max(image))
return new_image.astype(np.uint8)
def rgb_arithmetic_mean(image):
r,g,b = cv.split(image)
r = arithmetic_mean(r)
g = arithmetic_mean(g)
b = arithmetic_mean(b)
return cv.merge([r, g, b])
arithmetic_mean_img = rgb_arithmetic_mean(gauss_img)
plt.imshow(arithmetic_mean_img)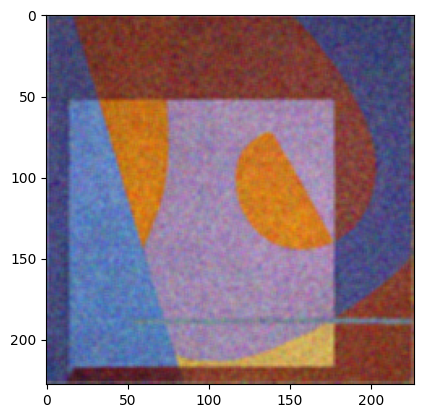
谐波
import scipy
import scipy.stats
def harmonic_mean_operator(roi):
roi = roi.astype(np.float64)
if 0 in roi:
roi = 0
else:
roi = scipy.stats.hmean(roi.reshape(-1))
return roi
def harmonic_mean(image):
new_image = np.zeros(image.shape)
image = cv.copyMakeBorder(image, 1, 1, 1, 1, cv.BORDER_DEFAULT)
for i in range(1, image.shape[0] - 1):
for j in range(1, image.shape[1] - 1):
new_image[i - 1, j - 1] = harmonic_mean_operator(image[i - 1: i + 2, j - 1: j + 2])
new_image = (new_image - np.min(image)) * (255 / np.max(image))
return new_image.astype(np.uint8)
def rgb_harmonic_mean(image):
r, g, b = cv.split(image)
r = harmonic_mean(r)
g = harmonic_mean(g)
b = harmonic_mean(b)
return cv.merge([r, g, b])harmonic_mean_img = rgb_geometric_mean(salt_img)
plt.imshow(harmonic_mean_img)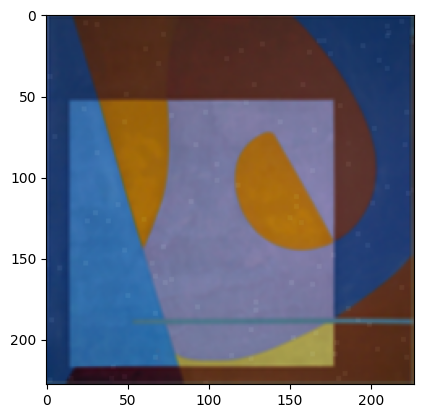
逆谐波
def iharmonic_mean_operator(roi, q):
roi = roi.astype(np.float64)
return np.mean((roi) ** (q + 1)) / np.mean((roi) ** (q))
def iharmonic_mean(image, q):
new_image = np.zeros(image.shape)
image = cv.copyMakeBorder(image, 1, 1, 1, 1, cv.BORDER_DEFAULT)
for i in range(1, image.shape[0] - 1):
for j in range(1, image.shape[1] - 1):
new_image[i - 1, j - 1] = iharmonic_mean_operator(image[i - 1: i + 2, j - 1: j + 2], q)
new_image = (new_image - np.min(image)) * (255 / np.max(image))
return new_image.astype(np.uint8)
def rgb_iharmonic_mean(image, q):
r, g, b = cv.split(image)
r = iharmonic_mean(r, q)
g = iharmonic_mean(g, q)
b = iharmonic_mean(b, q)
return cv.merge([r, g, b])iharmonic_mean_img = rgb_iharmonic_mean(salt_img, -2)
plt.imshow(iharmonic_mean_img)
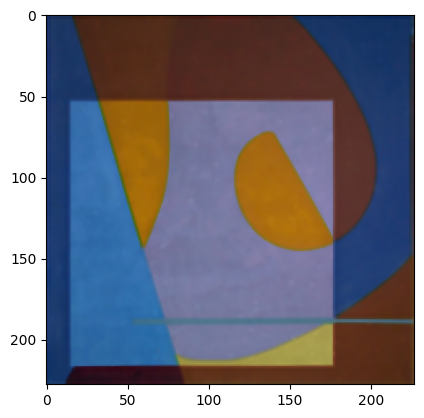
正文完